Spring CXF Rest Webservices Using JSON with Exception Handling
This is a simple tutorial on how to create a simple JAX-RS Web Service in Java using Spring and Apache CXF. This service will be follow the request/response pattern, it will using HTTP POSTs which are formatted JSON requests and it will produce JSON responses.
This will run on JBoss-Application Server v6.2. This will show you how to create a JAX-RS Web Service for managing User objects, you can fetch, insert, update and delete them. It will use an in-memory store to keep it simple.
Step 1: Create a new Maven web application project in java using eclipse. Add the below dependencies in your pom.xml.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-bundle</artifactId>
<version>2.7.6</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-asm</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.apache.geronimo.specs</groupId>
<artifactId>geronimo-jaxws_2.2_spec</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-server</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-continuation</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-http</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-io</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-util</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-security</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-frontend-jaxrs</artifactId>
<version>2.7.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-mapper-asl</artifactId>
<version>1.9.11</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core-asl</artifactId>
<version>1.9.11</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-jaxrs</artifactId>
<version>1.9.11</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3.RELEASE</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
In the above pom.xml i am excluding some of the dependencies from cxf-bundle for the better performance of our project.
Step 2: Create our
User Model for mapping our JSON request with our Application.
package in.springrestcxf.user;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String city;
private String state;
//getters and setters for above attributes.
}
Step 3: Create our
Response Model for sending back the response to client in JSON format.
package in.springrestcxf.response;
import java.util.List;
import org.codehaus.jackson.map.annotate.JsonSerialize;
import in.springrestcxf.user.User;
public class Response {
private String message;
//Use JsonSerialize for excluding non null and empty values in JSON response
@JsonSerialize(include=JsonSerialize.Inclusion.NON_EMPTY)
private User user;
@JsonSerialize(include=JsonSerialize.Inclusion.NON_EMPTY)
private List<User> users;
private boolean success;
//getters and setters
}
Step 4: Create our User Interface Which used to Map the rest request with our Application with JSON as Request and Response.
package in.springrestcxf.usermanager;
import in.springrestcxf.response.Response;
import in.springrestcxf.springexep.MyRestException;
import in.springrestcxf.user.User;
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.POST;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
public interface UserManager
{
@POST
@Path("/fetchUserById")
@Consumes({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
@Produces({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
public Response fetchUserById(User request);
@POST
@Path("/fetchAllUsers")
@Consumes({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
@Produces({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
public Response fetchAllUsers();
@POST
@Path("/insertUser")
@Consumes({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
@Produces({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
public Response insertUser(User request);
@POST
@Path("/updateUser")
@Consumes({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
@Produces({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
public Response updateUser(User request);
@POST
@Path("/deleteUser")
@Consumes({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
@Produces({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
public Response deleteUser(User request);
public User getUser(User request) throws MyRestException;
public Response processErrorCodes(MyRestException e) throws MyRestException;
}
In our User Interface we have four different operations for our user. We are producing and consuming JSON as request and response using @Produces and @Consumes Annotations. @POST use to specify our request as POST method.
1. Insert User (For inserting users in to ArrayList).
2. Fetch All Users(Fetch All users from the ArrayList that we have saved in Insert User).
3. Fetch User By Id(Fetch the particular user based on the id passed with our request).
4. Update User(Update the particular user based on the id).
5. Delete User(Delete the user from Array-list based on the id passed).
Step 5: Create our Implementation of our User Interface for writing for operations.
package in.springrestcxf.managerimpl;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import in.springrestcxf.response.Response;
import in.springrestcxf.springexep.MyRestException;
import in.springrestcxf.user.User;
import in.springrestcxf.usermanager.UserManager;
public class UserManagerImpl implements UserManager {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>(); //Put all the user request in list.
Response response = new Response(); //Send back the response.
public Response fetchUserById(User request) {
try
{
request = getUser(request);
if(request!=null)
{
response.setMessage("Your Employee Details");
response.setUser(request);
response.setUsers(null);
response.setSuccess(true);
return response;
}
response.setMessage("Employee Not Found");
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(null);
response.setSuccess(false);
}
catch(MyRestException springCxfException)
{
try {
processErrorCodes(springCxfException);
} catch (MyRestException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return response;
}
public Response fetchAllUsers(){
try
{
response.setMessage("Employee Details");
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(users);
response.setSuccess(true);
}catch(Exception exception)
{
response.setMessage(exception.getLocalizedMessage());
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(null);
}
return response;
}
public Response insertUser(User request){
try
{
users.add(request);
response.setMessage("Employee Inserted Successfully");
response.setUser(request);
response.setUsers(null);
response.setSuccess(true);
}
catch(Exception exception)
{
response.setMessage(exception.getLocalizedMessage());
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(null);
}
return response;
}
public Response updateUser(User request) {
try
{
User user = getUser(request);
if(user!=null)
{
user.setCity(request.getCity());
user.setEmail(request.getEmail());
user.setName(request.getName());
user.setState(request.getState());
response.setMessage("Employee Updated Successfully");
response.setUser(user);
response.setUsers(null);
response.setSuccess(true);
return response;
}
response.setMessage("Employee Not Found");
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(null);
response.setSuccess(false);
}catch(MyRestException springCxfException)
{
try {
processErrorCodes(springCxfException);
} catch (MyRestException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return response;
}
public Response deleteUser(User request) {
try
{
Iterator<User> it = users.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
User user = it.next();
if(user.getId()==request.getId())
{
it.remove();
//Delete the User object from list using iterator method.
response.setMessage("Employee Deleted Successfully");
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(null);
response.setSuccess(true);
return response;
}
}
response.setMessage("Employee Not Found");
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(null);
response.setSuccess(false);
}catch(Exception exception)
{
response.setMessage(exception.getLocalizedMessage());
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(null);
}
return response;
}
/*Check whether the User is present id list or not*/
public User getUser(User request) throws MyRestException {
try
{
for(User user : users)
{
if(user.getId()==request.getId())
{
return user;
}
}
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
throw new MyRestException(e.getMessage(), "Exception");
}
return null;
}
public Response processErrorCodes(MyRestException e)
throws MyRestException {
if(e.getErrorCode().equals("Exception"))
{
e.printStackTrace();
response.setMessage(e.getLocalizedMessage());
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(null);
}
else
{
e.printStackTrace();
response.setMessage(e.getLocalizedMessage());
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setUser(null);
response.setUsers(null);
}
return response;
}
}
In this class i wrote all my operations which implemented from my interface. I am using Array List for storing all the user details which get from our request and the list is used for further processing. I am having getUser() method for checking whether the user is present in list or not. This is common to all operations. I have my own Exception class which used to handle exceptions other than CXF exceptions and fault. If exception occurred i am calling processErrorCodes() method to return back the response with exception message and code. We will see how to handle CXF exceptions in our application in step 7.
Step 6: Create our own custom exception class which used to handle our exceptions in our application and we can process error-code and exception message and send it back to the client.
package in.springrestcxf.springexep;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class MyRestException extends Exception implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String errorCode="Unknown_Exception";
public MyRestException(String message, String errorCode){
super(message);
this.errorCode=errorCode;
}
public String getErrorCode(){
return this.errorCode;
}
}
Step 7: Create our own Exception class which used to handle CXF Exception while processing request and response. If any exception occurs during request or response processing this class will send back the response with status and exception message to the client. We need to implement ExceptionMapper which used to handle the exceptions.
For e.g while sending the request user didn't set the content-type as application/json, So while processing the request our custom class will catch the exception and send back the same to client.
We need to define the exception class in our configuration file under <jaxrs:providers>, So CXF will automatically map our exception class with our application.
package in.springrestcxf.springexep;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
import javax.ws.rs.ext.ExceptionMapper;
import javax.ws.rs.ext.Provider;
@Provider
@Produces({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
public class ExceptionHandler implements ExceptionMapper<Exception> {
public Response toResponse(Exception exception) {
Response.Status status;
status = Response.Status.BAD_REQUEST;
return Response.status(status).entity(exception.getLocalizedMessage()).build();
}
}
@Provider is to inform CXF that we have our own custom CXF exception class which used to handle all CXF exception in our application.
In the above exception class i implement ExceptionMapper with Exception class which used to handle all exceptions including RunTimeExceptions also. We can pass any kind of Exception inside ExceptionMapper based on our requirement.
Step 8: CXF configuration file(rest-content.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cxf="http://cxf.apache.org/core"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws"
xmlns:jaxrs="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxrs"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/core http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/core.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxrs http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxrs.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="in.springrestcxf"/>
<bean id="userManagerService"
class="in.springrestcxf.managerimpl.UserManagerImpl">
</bean>
<bean id="jsonProvider"
class="org.codehaus.jackson.jaxrs.JacksonJsonProvider"/>
<bean id="exceptionHandler"
class="in.springrestcxf.springexep.ExceptionHandler" />
<jaxrs:server id="userManagerREST" address="/user">
<jaxrs:serviceBeans>
<ref bean="userManagerService"/>
</jaxrs:serviceBeans>
<jaxrs:extensionMappings>
<entry key="json" value="application/json"/>
</jaxrs:extensionMappings>
<jaxrs:providers>
<ref bean="jsonProvider" />
<ref bean="exceptionHandler" />
</jaxrs:providers>
</jaxrs:server>
</beans>
In my configuration file i mapped my bean classes which used to configure with CXF for processing request, response and Exceptions. UserManagerImpl is my Service bean which used to map all the request and process response based on the data. I mapped my CXF exception handler class under <jaxrs:providers> in order to catch the exception and further send back the response to client. I am using the rest address as /user in order to map my request.
Step 9: web.xml
<web-app version="3.0"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
metadata-complete="true">
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>CXFServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>CXFServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/services/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/rest-content.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>
So here i mapped my servlet as CXF servlet which will start while our application started. and i mapped the url pattern as
/services/* which used to map my rest request.
Step 10: JBoss deployment structure(If you are deploying your application under JBoss)
<jboss-deployment-structure xmlns="urn:jboss:deployment-structure:1.2">
<deployment>
<dependencies>
<module name="org.codehaus.jackson.jackson-core-asl"/>
<module name="org.codehaus.jackson.jackson-mapper-asl"/>
<module name="org.codehaus.jackson.jackson-jaxrs"/>
<module name="org.slf4j"/>
</dependencies>
</deployment>
</jboss-deployment-structure>
It will load all the jars at run time of application.
Note: Jboss 6 or latest version's have their own JAX-RS and CXF servlet, So when you are running your application some collision between jar files will happen and you will get No Such Method Error while processing CXF related Exception. For over come that download the latest version of JBOSS jar files and put it inside your \jboss-eap 6.2\modules\system\layers\base folder. In my case i am using JBOSS 6.2 version which used to collide with my application jar files. So i downloaded the JBOSS rest easy jars of v3.0.9 and replace all the jars with my JBoss modules.
For more details refer http://stackoverflow.com/questions/24139097/resteasy-client-nosuchmethoderror
Step 11: Sample request and Response
1. http://localhost:8080/springrestcxf/services/user/insertUser
2. http://localhost:8080/springrestcxf/services/user/fetchAllUsers
3. http://localhost:8080/springrestcxf/services/user/fetchUserById
4. http://localhost:8080/springrestcxf/services/user/updateUser
5. http://localhost:8080/springrestcxf/services/user/deleteUser
Above is the URL which we are used to call rest service integrated with our appplication.
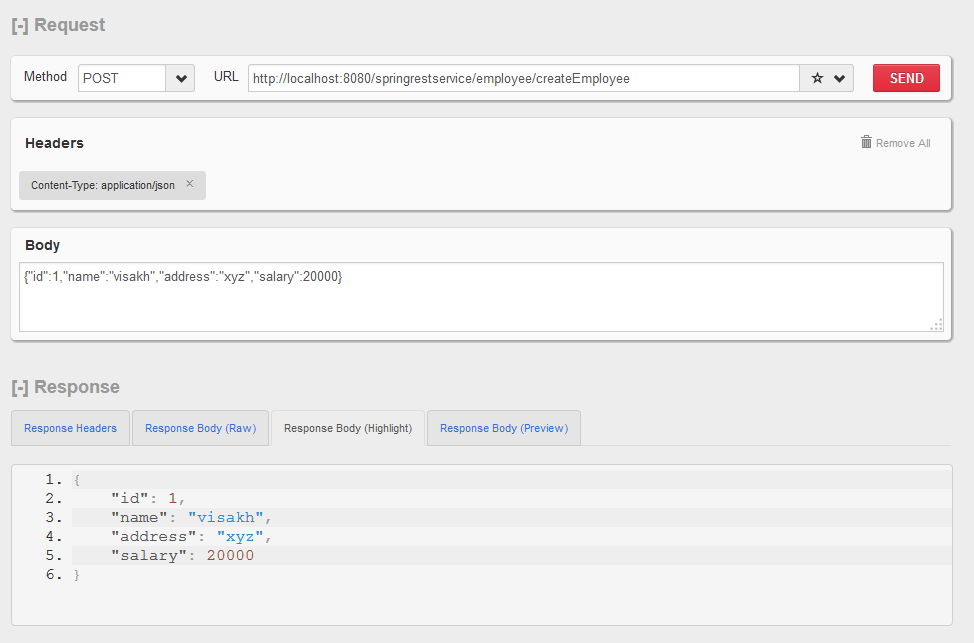
Insert User
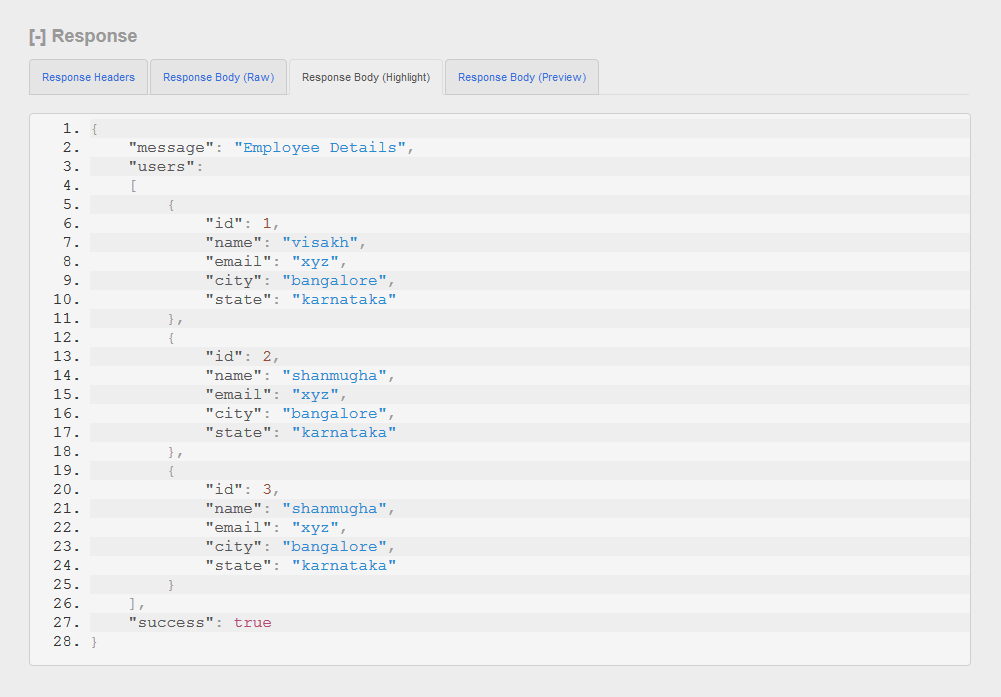
Fetch All Users(Input - {} )
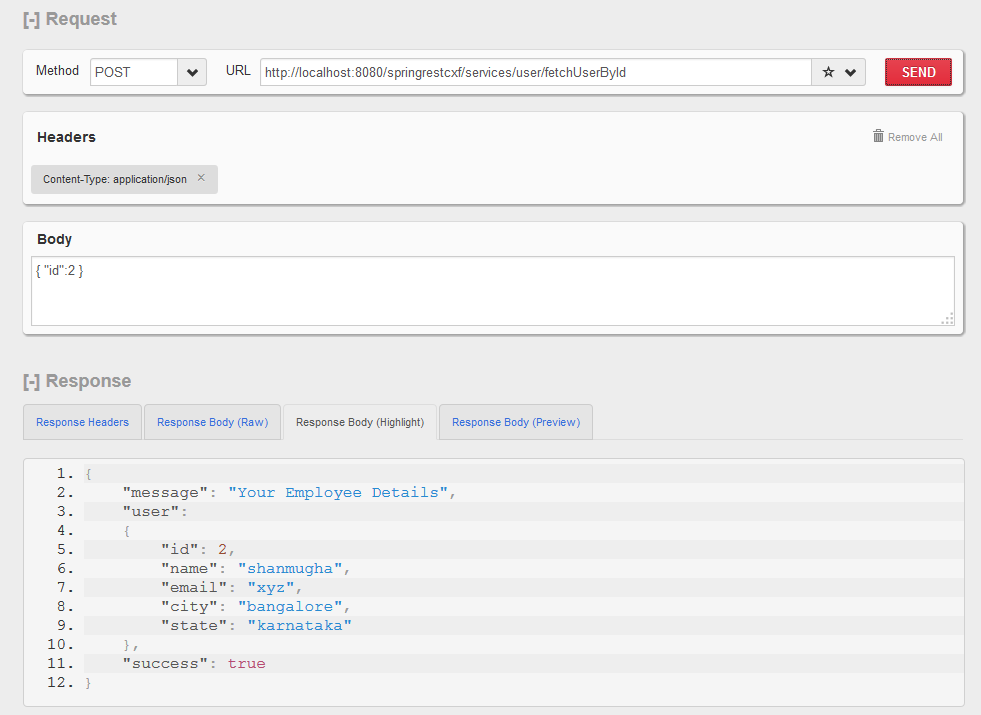
Fetch User by Id
Update User
Delete User
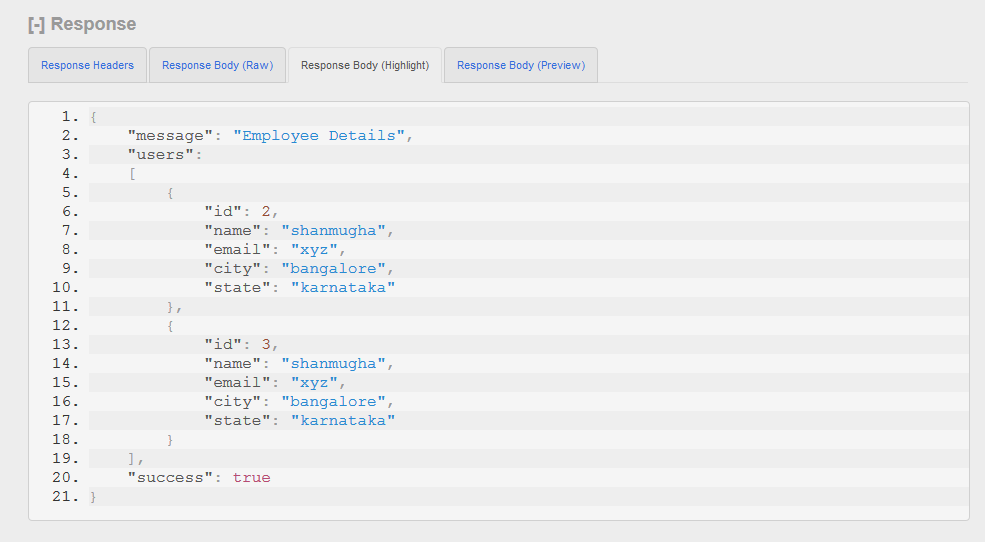
Fetch All users After Deleting particular user from list
CXF Exception while sending JSON request and validating the request inside CXF
In the above Screen shot you can able to see the exception return by our ExceptionHandler class that we created to handle CXF Exception. In the above request i am not passing the JSON data in a correct format. I put multiple commas in between the key and values, So while processing the request CXF transport validate the request and throws the exception to our custom class from there i am returning the status and exception happened in CXF transport. In the same way we can able to handle any Exception that happens inside CXF transport or Interceptors.
That's all Folks..
Hope you guys got good idea on CXF rest service Using Spring with Exception Handling.